To revel in Excel absolutely, you will have to know the way to make use of the IF-THEN serve as.
The IF-THEN is one among Excel’s maximum spectacular purposes, as you’ll be able to use it to investigate knowledge, draw inferences and make choices below sure preset prerequisites. However what precisely are IF-THEN statements, and the way are you able to get started the usage of them?
On this information, we’ll display you use IF-THEN statements to give a boost to your mastery of Excel.
Desk of Contents
- What are IF-THEN statements in Excel?
- The Advantages of IF-THEN Statements in Excel
- The best way to Use IF-THEN Statements in Excel
- Very best Practices for IF-THEN Statements in Excel
What are IF-THEN Statements in Excel?
IF-THEN statements are purposes in Excel that go back a singular set of movements after your preset situation is met.
Merely put, while you use the “If” observation, you’re surroundings a situation and teaching Excel to accomplish a singular set of movements when your preset situation is right and any other when the situation is fake.
To make use of the “If “ serve as in Excel, you get started by way of writing the equivalent signal (=), adopted by way of “if,” then your situation, and a two-part syntax teaching this system on what to do when your necessities are or aren’t met.
The syntax generally seems like this:
- =IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false])
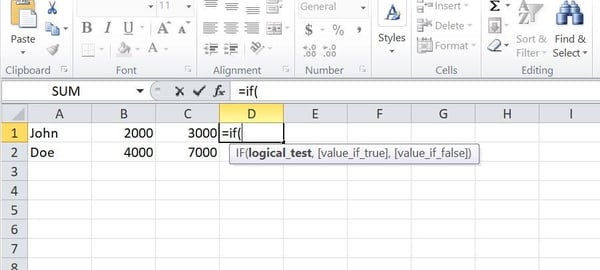
The “If” serve as is to hand, particularly in case you have a big knowledge quantity and wish to steer clear of the strain of computing formulation for each and every knowledge. Right here’s an instance of ways easy it’s to make use of IF-THEN statements in Excel:
On this instance, I’ve a spreadsheet containing 3 columns of knowledge. The place column A accommodates title knowledge, and columns B and C, comprise integer knowledge.
The use of the If serve as, I set a situation the usage of the syntax:
- =IF(B1>C1, “sure,” “no”)
This serve as initiates a command telling the Excel program to check if the knowledge price in mobile B1 is bigger than the knowledge price in mobile C1.
I’ve merely suggested Excel to present me a reaction of “sure” below the situation that the price of mobile B1 is bigger than mobile C1 and a reaction of “no” below the situation that the price of mobile B1 is lower than the price of mobile C1.
I then prolonged this serve as to the opposite respective cells the usage of a easy autofill trick. Take a look at our information on the usage of Excel like a professional for some useful tips to make your Excel enjoy more uncomplicated.
It’s necessary to notice that the IF-THEN observation handiest permits you to set a situation for 2 variables. That implies you’ll be able to handiest set prerequisites together with, say, the knowledge price in cells B1 and C1 or a situation together with knowledge values in mobile B1 and an outlined integer or textual content.
As an example, you’ll be able to set a situation teaching Excel to go back a reaction of “Sure” if the price in mobile B1 is bigger than the price of mobile B2 as proven within the instance above. Or, you’ll be able to set a situation asking Excel to go back the reaction ”sure” or “no” if the price of mobile B1 is bigger or lower than 1000.
Right here’s a snappy instance:
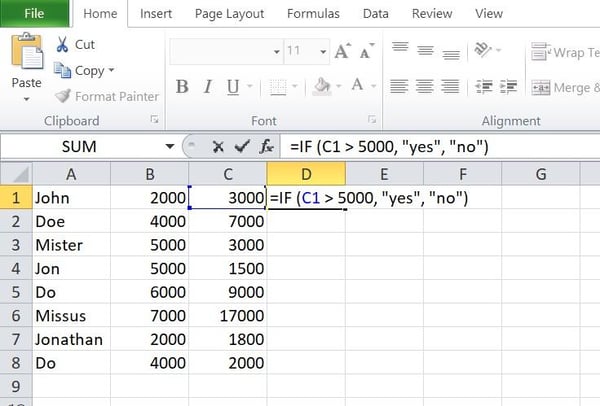
Right here, I advised Excel to go back the reaction “sure” if the knowledge price in mobile C1 is bigger than 5000 and “no” if the price is lower than 5000.
Right here’s the reaction Excel returned:
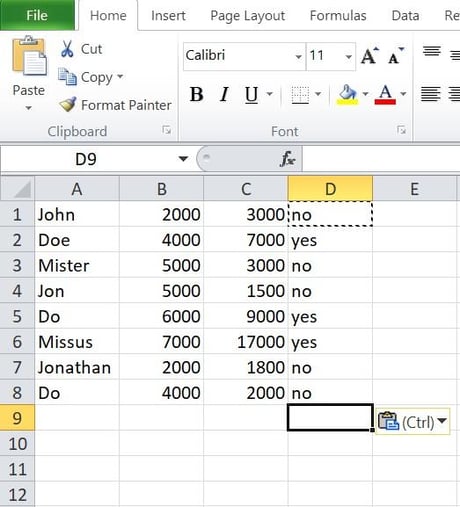
As discussed previous, the IF-THEN observation is an impressive Excel serve as with a lot of advantages. Studying to make use of this serve as correctly will astronomically build up your mastery of Excel.
The Advantages of IF-THEN Statements In Excel
Listed here are some advantages that IF-THEN statements in Excel can give you:
Checking for Mistakes in Knowledge
You’ll use IF-THEN statements to test for mistakes when inputting knowledge into the spreadsheet.
As an example, if you are feeling like you’ve made a mistake by way of inputting a bunch as a substitute of a textual content into your spreadsheet, you’ll be able to take a look at the usage of an if serve as:
- IF(B1 = “”, “Textual content”, “Quantity”)
Calculating Debt Time table or Depreciation Time table
Monetary Analysts can use IF-THEN statements to calculate debt and depreciation schedules.
The use of the IF-THEN observation, you’ll be able to set prerequisites asking this system to go back a reaction for months with remarkable balances or even draw up a compensation agenda.
For Budgeting
As a monetary analyst, the usage of IF-THEN statements would make budgeting more uncomplicated. IF-THEN purposes will will let you create as much as 64 prerequisites, which will lend a hand you for your budgeting procedure.
To Prepare Knowledge
The principle skill of IF-THEN statements is surroundings directions below sure prerequisites. Thus it’s simple to arrange knowledge for your spreadsheet below sure prerequisites the usage of if statements.
You’ll set prerequisites for a selected mobile field or more than one cells and prepare your spreadsheet knowledge below mentioned prerequisites.
Works Smartly With Different Formulation
A thrilling benefit of IF-THEN statements is their flexibility. Because of its flexibility, you’ll be able to use IF-THEN statements with different formulation in Excel.
As an example, you’ll be able to use it with the DATEVALUE() serve as, the SUM() serve as, and even the COUNT() serve as.
The best way to Use IF-THEN Statements in Excel
Now that what an IF-THEN observation is and the way it can get advantages you, your next step is understanding use it correctly.
There are two how to use the serve as, and we’ll get started with the fundamentals. First, right here’s a easy step by step process for writing IF-THEN statements in Excel.
Step 1: Click on at the mobile you need to layout, say mobile A1.
Step 2: Write the IF-THEN serve as formulation immediately into the mobile field.
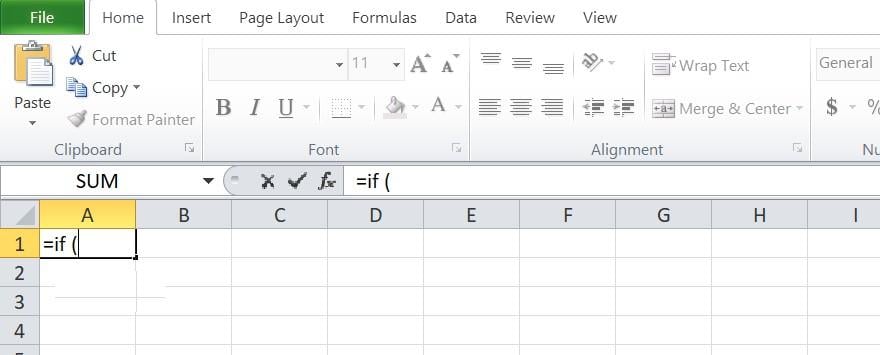
Or within the formulation field. 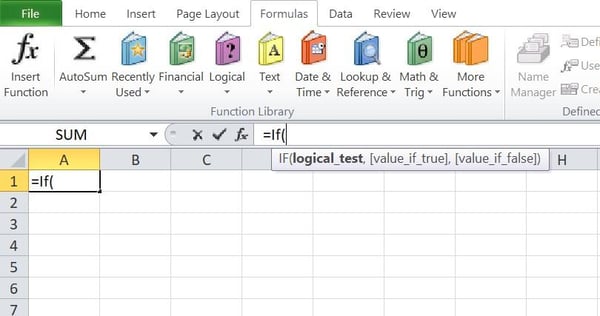
Step 3: Start writing your prerequisites and anticipated responses to mentioned prerequisites.
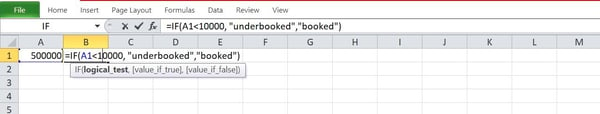
Keep in mind: At all times get started the formulation with an “equivalent” signal and enter the suitable punctuation so that you don’t get an error message after inputting the serve as.
Right here’s an alternate step by step you’ll be able to use.
Choice Step 1: Click on at the “Formulation” tab within the taskbar menu of your Excel program.
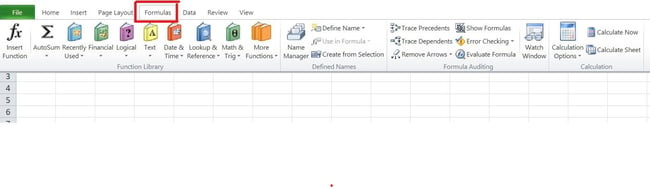
Choice Step 2: Click on at the “Insert Serve as” choice, which can release a conversation menu:
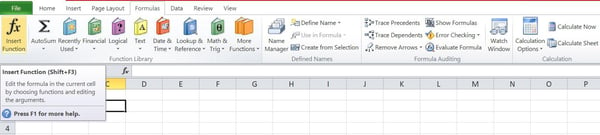
Choice Step 3: Make a selection “IF” from the checklist of choices within the conversation menu and click on “OK.” It is going to release a conversation field.
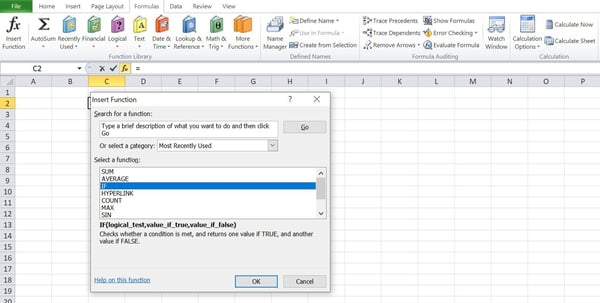
Choice Step 4: Within the conversation field, enter your situation and directions telling this system what solutions to go back when the situation is met and when it isn’t met.
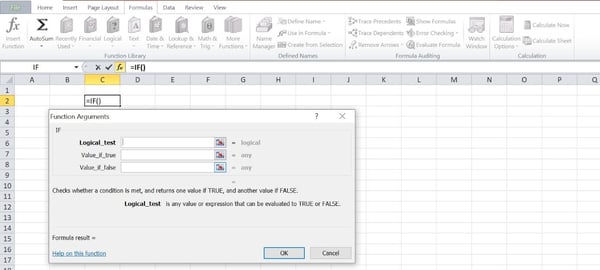
Observe: It’s higher to make use of the “Insert Serve as” approach in the event you’re writing a easy IF-THEN serve as, because it launches a formulation builder that can assist you get rid of the hazards of mistakes when inputting your formulation.
This system will robotically enter the suitable punctuations and codecs and handiest require you to enter your prerequisites and directions within the 3 fields of the conversation field.
Now that you understand how first of all the IF-THEN serve as, let’s assessment the opposite use circumstances for if purposes.
Writing IF-THEN Serve as for texts
IF-THEN purposes for texts are common IF-THEN purposes, however on this case, the serve as exams for a string of textual content after which returns a preset reaction relying on whether or not the situation is fulfilled.
The use of the IF-THEN serve as is slightly easy, and we’ve touched on it a couple of instances within the examples to this point. Alternatively, right here’s a step by step process for writing IF-THEN statements in Excel with textual content.
Step 1: Click on at the mobile field the place you need to insert the serve as.
Step 2: Write the “equivalent” (=) signal.
Step 3: Get started writing the if observation, along side the prerequisites for the take a look at and the responses to be returned.
Step 4: After writing the if observation, click on input.
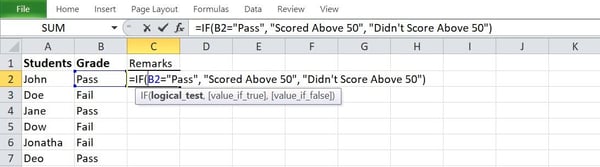
Right here’s an instance appearing generate a commentary pointing out who handed or failed a direction for a first-year elegance the usage of IF-THEN statements in Excel with textual content:
On this instance, the usage of the IF-THEN serve as:
- If(B2 = “Move,” “Scored above 50”, “Didn’t rating above 50”)
This system used to be requested to go back a reaction of “Scored above 50” or “Didn’t rating above 50” if the string of textual content in mobile B2 is the same as “Move.”
Alternatively, we will be able to take a look at the opposite direction round the usage of the serve as:
- If(B2 <> “Move,” “Scored above 50”, “Didn’t rating above 50”)
This system used to be requested to go back a reaction of “Scored above 50” or “Didn’t rating above 50” if the string of textual content in mobile B2 isn’t equivalent to “Move.”
Observe: At all times insert double citation marks when pointing out your textual content parameters.
IF-THEN statements are case-insensitive until differently said.
To make an IF-THEN observation case-sensitive, you will have to precede your situation parameters with the phrase “EXACT.” The use of the instance above, Excel will take a look at for uppercase textual content with this formulation:
- IF(EXACT(B2, “PASSED”), “Scored above 50”, “Didn’t rating above 50”)
Writing IF-THEN Purposes for Numbers
You will have to know the fundamental Excel operators and their indicators earlier than writing IF-THEN statements in Excel for numbers. Right here’s a information to Excel that can assist you be informed the fundamental Excel formulation, operators, and extra.
Apply those steps.
Step 1: Click on at the mobile field the place you need to insert the serve as.
Step 2: Write the “equivalent” (=) signal.
Step 3: Get started writing the if observation, along side the prerequisites for the take a look at and the responses to be returned.
Step 4: After writing the if observation, click on input. Your formulation will have to appear to be this:
- IF(B2>=50, “Handed”, “Failed”)
The use of the serve as above, we will be able to write an IF-THEN observation to test if a pupil handed or failed a direction. Right here’s an instance:
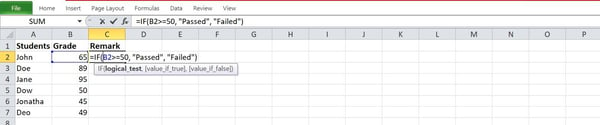
This serve as units a situation to check if mobile B2 accommodates an integer price more than or equivalent to 50. If this situation is met, this system will go back a reaction of “Handed” and a “Failed” reaction if the situation isn’t met.
Observe: IF-THEN purposes don’t handiest paintings for integers. They may be able to additionally paintings for actual numbers and destructive numbers.
Writing IF-THEN purposes for dates
Probably the most distinctive types of writing IF-THEN purposes is the date layout. Many of us might suppose they may be able to write IF-THEN purposes for dates like they write IF-THEN purposes for numbers.
Sadly, that isn’t so.
Because the Excel program can not learn the common date layout of mm/dd/yyyy, you’ll must insert the “DATEVALUE” serve as into your IF-THEN serve as to make the Excel program know that you just’re checking out a date situation.
Your serve as will have to appear to be this:
- IF(B2>=DATEVALUE(“mm/dd/yyyy”), “sure,” “no”)
Right here’s a step by step process on use this for your spreadsheet:
Step 1: On your spreadsheet, click on at the mobile the place you need to enter the serve as.
Step 2: Write the “equivalent” (=) signal.
Step 3: Get started writing the if serve as. Your syntax will have to glance one thing like this:
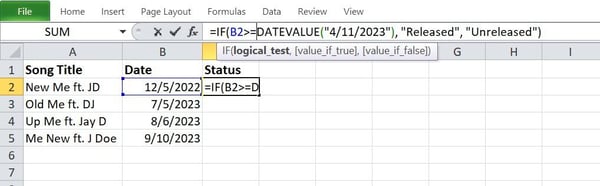
Step 4: Click on Input for your keyboard, and the serve as will go back a standing reaction of both “Launched” or “Unreleased.”
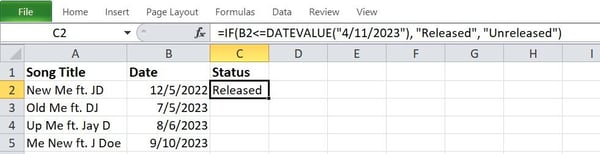
The serve as above exams whether or not the date in mobile B2 is bigger than the eleventh of April 2023. The serve as will give a “Launched” or “Unreleased” reaction relying on whether or not the prerequisites are met or no longer.
Observe: You’ll set the IF-THEN serve as to check in opposition to the present date by way of inputting the TODAY() serve as into your IF-THEN serve as.
That is what your serve as will have to appear to be:
- IF(B2>TODAY(), “Launched”, “Unreleased”)
Writing IF-THEN Purposes for More than one Stipulations (Nested IF statements)
More than one IF-THEN statements or Nested if statements, as usually known as, will let you upload more than one if statements into one if observation.
A Nested if observation will appear to be this:
- IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], if(logical take a look at, [value_if_true], if(logical take a look at, [value_if_true], [value_if_false])))
For those who sought after to jot down an IF-THEN serve as to assign remarks to rankings of first-year scholars in a selected direction. Right here’s how to do that in a couple of steps:
Step 1: Click on at the mobile field the place you need to insert the serve as
Step 2: Write the “equivalent” (=) signal.
Step 3: Start writing the IF-THEN serve as. Your serve as will have to glance one thing like this:
- IF(B2>90, “Very good”, IF(B2>=80, “Very Excellent”, IF(B2>=70, “Excellent”, IF(B2>= 50, “Truthful”, “Deficient”))))
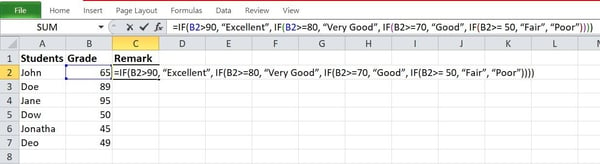
Step 4: Click on the Input key to obtain a reaction for your serve as.
The serve as will go back a reaction of “Very good” for college students who rating 90 or above; “Very Excellent” for college students who rating between 79 and 90; “Excellent” for college students who rating 69 and 80; “Truthful” for college students who rating between 49 and 70; and “Truthful” for college students that rating under 50.
Very best Practices for IF-THEN Statements in Excel
Listed here are some practices to apply to get the most productive from your IF-THEN purposes in Excel.
At all times use parentheses.
The easiest way to steer clear of mistakes for your formulation in Excel is by way of the usage of parentheses. Subsequently, if you need your if observation to serve as correctly, be sure to use parentheses accurately.
As an example, when writing more than one conditionals or a nested if observation, be sure to use parentheses in the proper puts to steer clear of “#NAME?” mistakes.
Use vary as a substitute of cells.
While you use Vary as a substitute of Cells, you’ll be able to steer clear of mistakes coming up when mobile knowledge adjustments or your formulation must be adjusted.
Write out each and every phase as its personal formulation.
It will sound useless, however writing each and every spreadsheet phase as its personal formulation would make your knowledge extra readable and more uncomplicated to grasp.
Any other get advantages to doing that is that you’ll be able to in finding the entirety you wish to have in a single position and edit it consistent with your wishes.
Much more, if there’s an error together with your serve as, writing each and every phase as its personal formulation makes it more uncomplicated so that you can debug and in finding any mistakes for your formulation.
By no means hesitate to make use of different formulation.
One improbable factor about Excel is that it allows you to use more than one purposes by way of putting them into one any other.
Like different formulation in Excel, you’ll be able to insert different purposes into your IF-THEN serve as to get the most productive out of it.
The use of your IF-THEN serve as along different formulation makes it more uncomplicated to make calculations, saves time (particularly while you’re running with huge knowledge), and makes it simple to identify any mistakes.
Getting Began
IF-THEN statements are sure to make your existence more uncomplicated. Even if it can be tough to seize the entirety directly, you can in finding it simple with consistent observe and steady use.
So don’t hesitate to discuss with this information anytime you face a problematic IF-THEN observation problem.
![]()

![Download 10 Excel Templates for Marketers [Free Kit]](https://wpfixall.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/9ff7a4fe-5293-496c-acca-566bc6e73f42.png)
